41 which label represents the coding part of dna?
Parts of a Graph | Overview, Labels & Examples - Video & Lesson ... Parts of a graph that are very useful to identify are the x and y-intercepts. They are found along the axes. They represent the values of one variable when the other is zero. X-intercepts are also ... Sandwalk: Editing the Wikipedia article on non-coding DNA The Wikipedia police have restored the original version three times without explaining why they think we should mention the ENCODE results in the introduction to an article on non-coding DNA and without explaining why Nessa Carey's book needs to be referenced. The group that's objecting includes Ramos1990, Qzd, and Trappist the monk.
Unique molecular CODE: Paramagnetic encoding of molecules Four elements provide 65,535 codes, and with only six we could, for example, label with unique codes all the euro banknotes currently in circulation. Considering that we can use twelve of these...
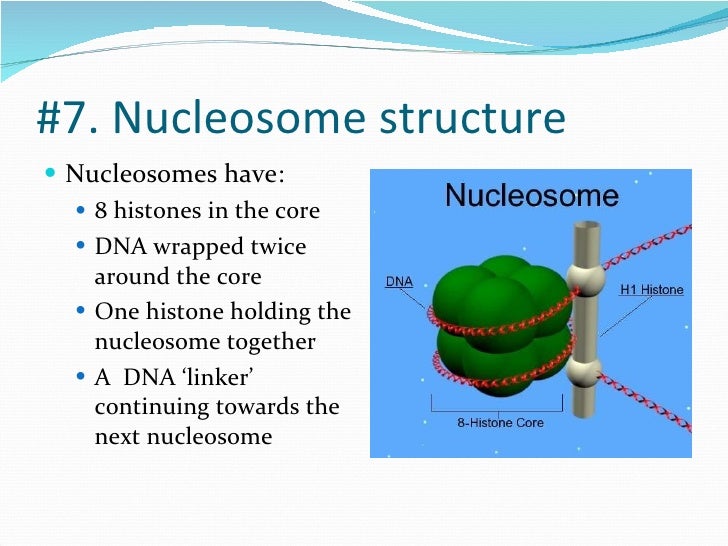
Which label represents the coding part of dna?
Central Dogma- Replication, Transcription, Translation The dogma is a framework for understanding the transfer of sequence information between information-carrying biopolymers, DNA and RNA (both nucleic acids), and protein. There are 3×3=9 conceivable direct transfers of information that can occur between these. The dogma classes these into 3 groups of 3: A. Three general transfers An Introduction to DNA Transcription - ThoughtCo DNA transcription is a process that involves transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNA. The transcribed DNA message, or RNA transcript, is used to produce proteins. DNA is housed within the nucleus of our cells. It controls cellular activity by coding for the production of proteins. Interphase- Definition, Stages, Cell cycle, Diagram, Video The synthesis (S) phase is the phase of cell copying or cell duplication of its DNA of its entire genome. Gap 1 (G1) This is the phase in which the cell undergoes normal growth and cell function synthesizing high amounts of proteins. The cell increases in size and volume as more cell organelles are produced.
Which label represents the coding part of dna?. Dna Coloring Transcription And Translation Pdf Answers Learn about the biology topic Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function in this free and fun science study guide! Dna And Genes Worksheet Answers ready to download or print. Crossword Puzzle, Life Science Crossword. Bottom dna code filename representation for each example, you are to provide a transcription. Line up as a team. Alden Edward, Sayer ... What Is DNA? Summary, Structure, and Importance - Healthline The sugar in DNA is called 2-deoxyribose. These sugar molecules alternate with the phosphate groups, making up the "backbone" of the DNA strand. Each sugar in a nucleotide has a nitrogen base... Applying: Given the following DNA sequence from the ... - Brainly.com This is the transcription process and occurs in the nucleus. When the DNI molecule separates into two strands to form the transcription bubble, we can identify two separate segments: coding strand and template strand. The coding strand goes in direction 5´ to 3´, while the complementary strand -template strand- grows in direction 3´ to 5. New approach can add diversity to crop species without breeding GMOs White represents chloroplast DNA. The letter C is highlighted for editing (with scissors) because the ptpTALECD enzyme makes point mutations by turning specific GC pairs in the DNA code into AT ...
Base Pair - Genome.gov DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) [GWA-NeeN] or thymine (T). DNA Replication: The Leading Strand and DNA Polymerase Activities DNA polymerase makes short lengths of DNA that are then bound together by DNA ligase. Learn how these enzymes work together to aid in DNA replication. Updated: 10/05/2021 Codon Recognition: How tRNA and Anticodons Interpret the Genetic Code Review of Codon Recognition. Translation is the process of converting the genetic information in the mRNA strand to the form of a protein. The basic unit of this genetic information is a codon. Transcription of DNA - Stages - Processing - TeachMePhysiology DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase. This mRNA then exits the nucleus, where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA. By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression.In this article we will look at the process of DNA ...
Double Helix - Genome.gov Double helix, as related to genomics, is a term used to describe the physical structure of DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder in a helix-like shape. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Cladogram- definition, features, parts, examples (vs Phylogram) Cladograms are generated by the analysis of morphological characters of the organisms and DNA or RNA sequencing data. Recently, however, computational phylogenetics is also used in the combination of the existing characters for the generation of cladograms. Cladograms are the assumptions for the preparation of phylogenetic trees. The human genome is, at long last, complete | Hacker News In many ways, non-coding DNA is just as important as the parts of the genome that code for proteins. Non-coding DNA determines expression levels, genome confirmation (shape), and replication efficiency among other things. The term junk DNA misleads students into thinking that these sections of DNA play little part in how a cell functions. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) - Genome.gov Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix.
Gene - Wikipedia In biology, a gene (from Greek: γένος, génos; [1] meaning generation [2] or birth [1] or gender) is a basic unit of heredity and a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that encodes the synthesis of a gene product, either RNA or protein. [3] [4] [5] During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA.
DNA sequencing - Wikipedia DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence - the order of nucleotides in DNA.It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine.The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.
Genetic Code - Genome.gov Genetic code. The story of the genetic code is the story of biology and genetics in the 19th, 20th, and 21st centuries, as well as its promises and its perils. Oswald Avery in 1944, for example, proved that the genetic code — that DNA —was indeed the carrier of hereditary information, ending more than 80 years of productive speculation.
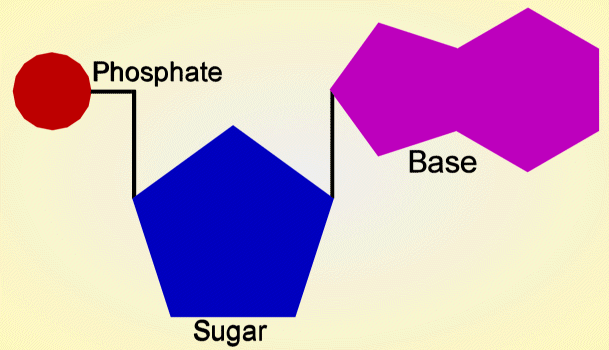
What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The structure ofDNA's can be visualized or thought of like a ladder. If we continue with this analogy, each "step or rung" of this ladder is made up of a string of nucleotides, in a very specific and controlled order.
Genetic Code Table Answer Key - Inrepsara Mar 5, 2021 — The answer is the genetic code. The genetic code consists of the sequence of nitrogen bases—A, C, G, U—in an mRNA chain. ... To find the amino acid for a particular codon, find the cell in the table for the first and second .... Oct 18, 2004 — The genetic code is degenerate. ...


Post a Comment for "41 which label represents the coding part of dna?"